Maryland NMLS Test Prep | Updated 2026
Pass the Maryland NMLS test! Take unlimited Maryland NMLS practice tests, crafted by an expert mortgage instructor to meet or exceed the difficulty of the actual SAFE MLO exam.
Don't rely on the outdated material on other Maryland NMLS exam prep sites! Our online Maryland practice NMLS test questions are up to date with the latest 2026 rules and regulations. Our NMLS practice tests are simulated national exams with uniform state content that apply to your state!
Our Maryland mortgage test prep comes with over 1,000 NMLS practice exam questions with detailed answer explanations. Our MLO test prep program also comes with mortgage term & definition flashcards, a comprehensive video learning series, an additional 100 mortgage math test questions, and comes with a 100% Pass Money-Back Guarantee!
Maryland NMLS Practice Tests
OUR SAFE MLO EXAM PREP INCLUDES...
"This program thoroughly prepares you to pass the NMLS test!" - Calvin T.
"I passed the NMLS exam on the first try with a 92!" - Jenn E.
Pass The NMLS Exam - 100% Money-Back Guarantee

1,000 NMLS Practice Test Questions
8 Mortgage Tests & NMLS Exam Vocabulary Flashcards

50 Additional MLO Math Practice Questions
All Mortgage Math Topics Will Be Covered

User Friendly Dashboard On All Devices
Take Exams in Practice Mode, or Live Exam Mode!

Facebook Support Group
Q&A With Expert Mortgage Teacher
Pass The Maryland NMLS Exam
Pass the MLO exam guaranteed! Our mortgage test prep has helped thousands of test-takers pass their mortgage loan originator test, and comes with a 100% Pass Money-Back Guarantee! Our MLO test prep comes with 1,000 SAFE exam questions up to date with the latest 2026 rules and regulations, 100 additional mortgage math questions, NMLS vocabulary flashcards, NMLS test prep videos, and reliable support from an expert MLO instructor.
Mortgage Test Topics: Federal Mortgage-Related Laws, General Mortgage Knowledge, Mortgage Loan Origination Activities, Ethics, and Uniform State Content - Pass The Maryland NMLS Exam!
Study For The NMLS Test On-The-Go!
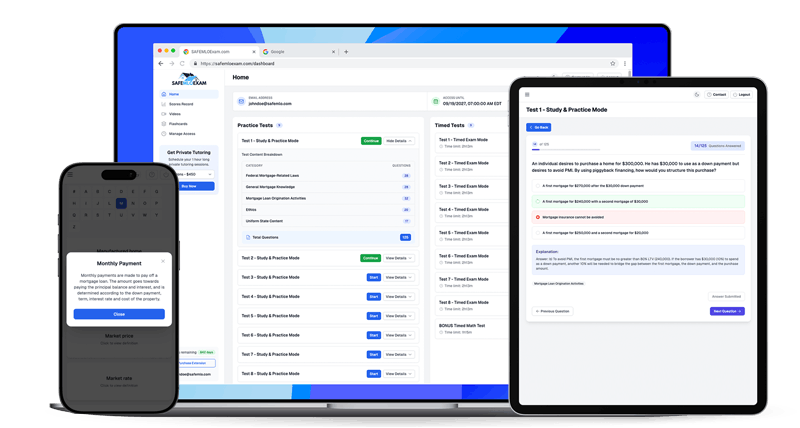
Log-In To Start Studying For Your NMLS Test
Watch Our SAFE MLO Exam Study Tip Videos
Maryland NMLS TEST PREP
